IoT und Industrie – Effizienz steigern durch Vernetzung
Der Weg zur Industrie 4.0 mit IoT
Erfassung von Echtzeitdaten, Verwaltung und Überwachung von Maschinen aus der Ferne, gesenkte Kosten und optimierte Verfügbarkeit der angeschlossenen Maschinen – das IoT in der Industrie möglich.
Sprechen wir von dem sogenannten Internet der Dinge und der Industrie 4.0 handelt es sich speziell um die Digitalisierung von alltäglichen industriellen Prozessen. Dazu gehört die smarte Vernetzung und Automatisierung von Geräten und Maschinen und natürlich auch eine effiziente und zuverlässige Datenverarbeitung. Mit uns von M2M Allnet haben Sie einen Partner an der Seite, der Ihnen sowohl SIM-Karten als auch die passenden Tarife zur Seite stellt. Kommen Sie also noch heute auf uns zu!
- Digital networking
- Lowered costs
- Live data
- Remote service
- Resource planning
IoT SIM-Karten von M2M Allnet
Standard SIM
Network all your smart IoT devices, across all networks, transnationally with M2M Allnet!
Industry SIM
Stay actionable everywhere and connect all industrial machines worldwide with M2M Allnet

eSIM
The successor to the classic SIM card, permanently installed in the end device. With all the familiar advantages!
Mit den richtigen IoT-Lösungen die Industrie voranbringen
Das Internet der Dinge oder IoT spielt im Leben vieler Menschen eine zentrale Rolle. Es geht darum, smarte Systeme effizient zu vernetzen und so Arbeitsabläufe und Prozesse zu erleichtern. Mit der vierten Revolution – der Industrie 4.0 – wird IoT nun auch für die Produktion oder Logistik interessant. Besonders die Vernetzung und Automatisierung stehen bei diesen neuen Entwicklungen im Vordergrund. Mit der Vernetzung von Systemen ist das Austauschen von Daten und Informationen möglich, die automatisch und smart aufeinander reagieren können.

Die Automatisierung wird in Zukunft die zentrale Steuerung von Geräten und Maschinen ersetzen. M2M-Maschinen funktionieren bereits dank moderner SIM-Karten intelligent und effizient. Bei uns von M2M Allnet können Sie Ihre Assets direkt über das Verwaltungsportal sparen, ohne vor Ort manuelle Anpassungen vorzunehmen.
The connection of hardware and software plays a central role here. Another step towards successful digitalisation is the miniaturisation of hardware components. The big goal is for devices and machines to work together in an automated and smart way in the future. This will reduce costs, avoid errors and enable real-time logistics and production.
The right tariff for all sectors - we have it!
IoT in der Industrie 4.0 – die Vorteile für Produktion und Co.

Das Ziel von Unternehmen mit Produktionsstätten ist es, die Stückzahl effizienter zu gestalten bei minimierten Herstellungskosten. Um diese besser zu erreichen, ist der Einsatz von IoT in der Industrie sinnvoll und produktiv.
Der Schlüssel hierzu ist der digitale Datenaustausch. Durch diesen wird der Fertigungsprozess effizienter gestaltet und gleichzeitig wird der Aufwand von Planung minimiert. Dies waren jedoch noch längst nicht alle Vorteile. Arbeiten Sie mit uns von M2M Allnet und unseren Industrie-SIM-Karten zusammen profitieren Sie durch folgende Vorzüge:
- Increases Efficiency saves resources
- Digital Data Exchange in real time
- Processes and Personnel Planning are optimized
- Best Networking and automation
- Intelligent Action through up-to-date information
- Flexibility Increased to save costs
Bei all den Vorzügen sind doch immer noch viele Unternehmen am Zweifeln, ob durch IoT in der Industrie keine Sicherheitslücken entstehen. Wir können Sie jedoch beruhigen. M2M bietet Sicherheit durch eine zentrale Verwaltung über unser Portal. Hier können Sie im Falle von Cyber-Angriffen schnell reagieren und betroffene Datenkarten deaktivieren, bevor Informationen gestohlen oder missbraucht werden können.
Questions? We are here for you!
Mit unseren IoT-Karten Ihre Produktivität steigern
Mit dem Einsatz von M2M-Karten für IoT in der Industrie wird eine Echtzeit-Datenübertragung und Kommunikation gewährleistet. Zeitgleich werden verschiedene Prozesse optimiert. Geräte und Maschinen sind z.B. in der Lage, bei einem Minimalbestand von Materialien, diese sofort automatisiert nachzubestellen.
Durch automatisierte Kommunikation ist es den einzelnen Komponenten möglich, problemlos Prozesse durchzuführen. Und auch die sogenannte Predictive Maintenance – prädiktive Instandhaltung – wird ermöglicht. Die jeweiligen Anwendungen, die beispielsweise mit einer IoT eSIM ausgestattet sind, lernen von Daten und stellen anhand dieser Prognose an. Dadurch wird die Effizienz gesteigert und manuelle Maßnahmen minimiert.
Mit dem Einsatz von Predictive Maintenance sind vorbeugend ein smarter Service, Maschinenwartung und Instandhaltungen möglich. Wollen Sie ebenfalls Ihre Industrie mit IoT neu und effizienter gestalten, dann sind Sie bei uns genau richtig. Dank unserer M2M SIM cards and M2M Allnet SIM cards. machen wir es Ihnen einfach, Teams, Maschinen und Geräte optimal zu vernetzen und smart zu arbeiten.

Für mehr Flexibilität IoT in der Industrie nutzen
Durch die autonomen Systeme werden in Zukunft individuelle Kundenwünsche kostenreduziert bewerkstelligt. Produktionsstätten sind dank neuer Fertigungs- und Informationstechnologien effektiver und flexibler – ein Prinzip, welches besonders bei 3D-Druckern deutlich wird.

Auch die Ortsunabhängigkeit bringt mehr Flexibilität in der Industrie mit IoT. Betriebe können global agieren, ohne Nachteile zu fürchten. Geräte und Maschinen kommunizieren zudem nicht nur untereinander, sondern auch mit anderen Systemen. Alle zugehörigen Komponenten wie Produktion, Entwicklung, Vertrieb, aber auch Kunden und Lieferanten werden so effektiv vernetzt. Ergänzt wird dies durch spezifische IoT-Plattformen, die eine zentrale Nutzung ermöglichen.
Mit SIM-Karten IoT und Industrie effizient gestalten
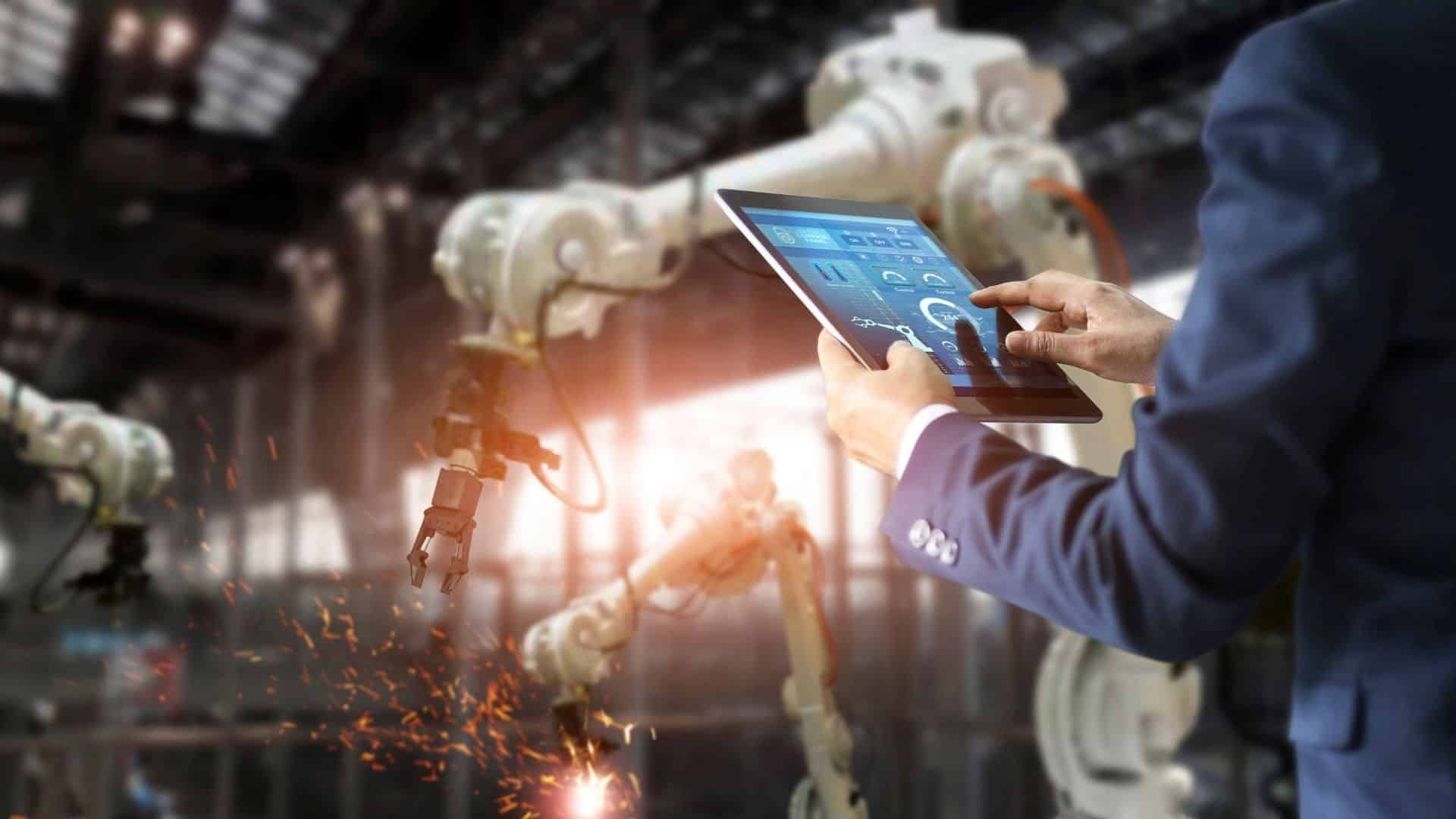

IoT bringt für die Industrie eine signifikante Effizienzsteigerung. Unter anderem helfen bei dem Prozess der Minimierung spezielle Funknetze – die sogenannte Narrowband-IoT und digitale Funktechnologien, wie sie in RFID-Chips integriert sind. RFID ist eine Technologie für Sender-Empfänger-Systeme und wird beispielsweise bei Tür-Transpondern eingesetzt.
Narrowband-IoT sorgt dafür, das Daten und Informationen ohne Frequenzbänder übertragen werden. Hier werden Datenkarten in Maschinen und Mobilgeräte eingesetzt, die in einem stetigen Austausch stehen. Dadurch werden Netze nicht mehr überlastet und eine reibungslose Zusammenarbeit gewährleistet. Wollen Sie ebenfalls durch diese IoT-Lösung in der Industrie profitieren, brauchen Sie einen Partner, der eine lückenlose Netzabdeckung gewährleisten kann – und genau deswegen sind Sie bei uns von M2M Allnet genau richtig. Durch unsere M2M-Tarife und Zusammenarbeit mit Partnern wie Telefonica, Telekom und Vodafone machen wir eine zuverlässige Verbindung zwischen Teams und Maschinen möglich. Mit uns gelingt die Implementierung Ihres Narrowband-IoT!
Contact us if you have any questions!
IoT in der Industrie verwenden und durchstarten
IoT setzt in der Industrie neue Standards und eröffnet Chancen, von denen Unternehmen und Betriebe deutlich profitieren. Zu diesen gehören unter anderem:
✓Durch automatisierte Kommunikation werden Daten und Informationen zuverlässig ausgetauscht.
✓Vorgesehenes Personal wird eingespart und an anderer Stelle eingesetzt.
✓ Dank direkter Kommunikation werden Aufträge genauer geplant und umgesetzt.
✓Kundenwünsche lassen sich einfacher und kostenreduzierter abbilden.
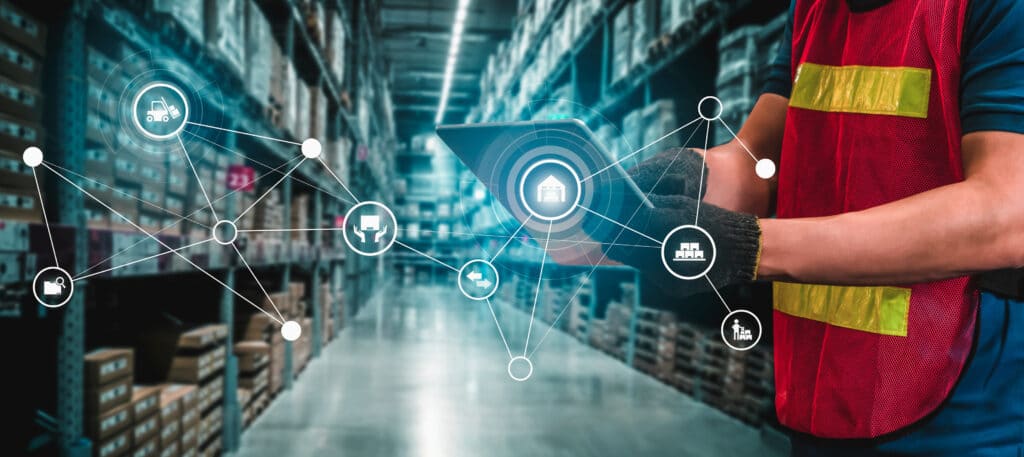

Allgemein gilt für IoT und Industrie: Je mehr Daten von einem System gesammelt werden, desto schneller lernt der Algorithmus und ist in der Lage, sich selbst zu optimieren – so funktioniert Big Data. Um wettbewerbsfähig zu bleiben, sollten moderne Betriebe daher frühzeitig nach Lösungen suchen, die Ihnen diese Vorteile bieten. Bei M2M Allnet unterstützen wir Sie gern dabei durch unsere Expertise und unser Leistungsangebot!
Mit IoT Kosten für Ihre Industrie reduzieren
Durch Automatisierung und Vernetzung werden menschliche Ressourcen eingespart. Bisherige manuelle Tätigkeiten wie Analysen oder Optimierungen werden zukünftig von miteinander vernetzten Geräten und Maschinen getätigt. Das heißt aber nicht, dass Menschen nun überflüssig sind. Sie können dank IoT in der Industrie Ihre personellen Ressourcen effizient umverteilen und so Ihre Arbeit produktiver gestalten.
Des Weiteren hilft eine umfassende Vernetzung Ihrer Assets auch dabei, die Umwelt zu schützen. Unzählige Transporte von Produkten und Materialien und überfüllte Lager stellen heutzutage eines der größten Probleme unserer Zeit und die Umwelt dar. Mit Industrie 4.0 sind dank smarter Kommunikationssysteme zwischen Geräten und Maschinen Echtzeit-Logistik und -Produktion möglich. So werden dank IoT in der Industrie nur so viele Güter wie nötig produziert, die Umwelt geschützt und monetäre Ressourcen gespart.
Optimiert, effizient, produktiv – IoT für die Industrie von Morgen

Smart Factory bringt viele Vorteile mit sich – vor allem wird der Einsatz von Ressourcen erheblich optimiert. Auch die Transparenz von Kosten steigert die Effizienz. Große Datenmengen werden durch Business-Intelligence-Systeme einfacher erfasst. Und auch das Überführen von Lagerbeständen oder einem kompletten Lager in ein anderes Land wird durch die Systeme einfacher und ressourcenschonend.
Durch die innovative Verknüpfung innerhalb eines IoT-Netzwerkes in der Industrie werden nicht nur Abläufe flüssiger und Fehler reduziert, sondern auch Bürokratie und Nachhaltigkeit werden parallel optimiert. Egal, ob IoT-Hardware oder Software mit uns von M2M Allnet als Ihren kompetenten Partner, wird Ihre Industrie durch fortschrittliche IoT-Lösungen auf ein neues Level gehoben. Hierfür stellen wir Ihnen eine großflächige Netzabdeckung, ein zentrales Verwaltungsportal und skalierbare Tarife zur Verfügung. Nutzen Sie also noch heute die Chancen der Industrie 4.0 für Ihre Industrie von morgen!
IoT - Themen für Industrie und Co.